The Role of Hormones in PCOS: What Every Woman Should Know
Share
Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common yet complex hormonal disorder that affects millions of women worldwide. It's characterized by a variety of symptoms, such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, weight gain, and excess hair growth. At the heart of PCOS are hormonal imbalances that can significantly impact a woman’s health and well-being. Understanding these hormonal dynamics is crucial for managing PCOS effectively.
What is PCOS?
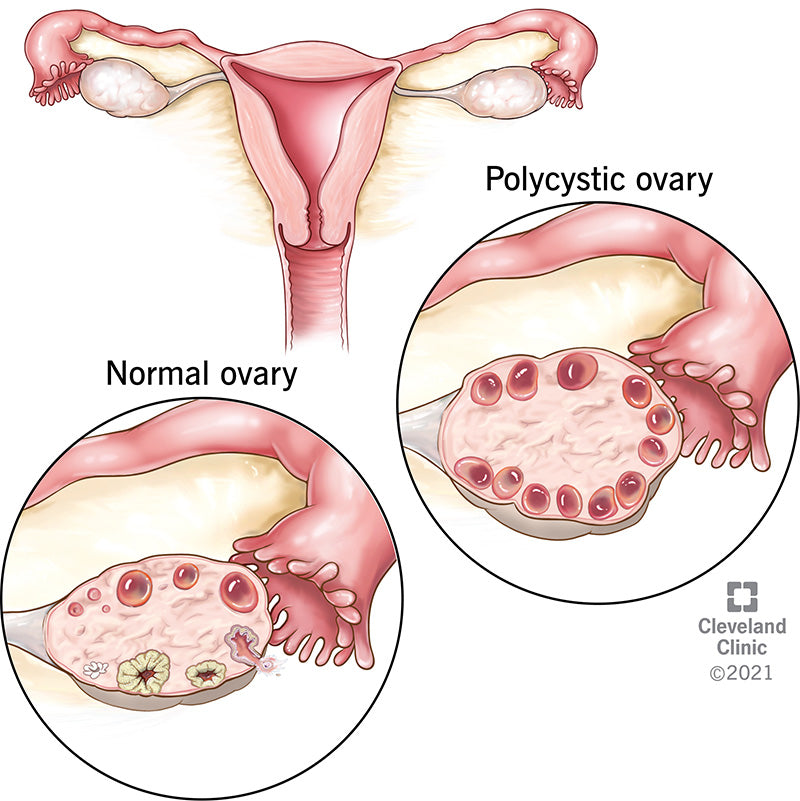
PCOS is a condition where a woman’s ovaries produce an abnormal amount of androgens, which are male sex hormones usually present in women in small amounts. The term "polycystic ovary" refers to the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, which can be detected through ultrasound. However, not all women with PCOS have these cysts, and not all women with ovarian cysts have PCOS. The condition is often diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms, hormonal tests, and ultrasounds.
How Hormonal Imbalances Play a Role
Hormonal imbalances are at the core of PCOS. Here’s a closer look at how specific hormones are involved:
- Androgens:
- Role: Androgens are often referred to as "male hormones," but they are present in women in smaller amounts. In PCOS, the ovaries produce higher than normal levels of androgens.
- Impact: High levels of androgens can cause symptoms like acne, hirsutism (excess hair growth on the face and body), and irregular menstrual cycles.
- Insulin:
- Role: Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, meaning their cells don’t respond well to insulin.
- Impact: To compensate, the body produces more insulin, which can lead to higher androgen levels and weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
- Progesterone:
- Role: Progesterone is essential for regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining pregnancy.
- Impact: Women with PCOS often have lower levels of progesterone due to infrequent ovulation, leading to irregular periods and fertility issues.
- Estrogen:
- Role: Estrogen is crucial for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system.
- Impact: Although women with PCOS may have normal or high levels of estrogen, the balance between estrogen and progesterone is often disrupted, contributing to menstrual irregularities.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of PCOS
Common Symptoms:
- Irregular periods or no periods at all
- Heavy periods
- Excessive hair growth (hirsutism)
- Acne and oily skin
- Weight gain, especially around the abdomen
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Difficulty getting pregnant
Diagnosis: Diagnosing PCOS usually involves a combination of the following:
- Medical History: Discussing symptoms and menstrual cycle irregularities.
- Physical Exam: Checking for signs like excess hair growth, acne, and weight gain.
- Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels, including androgens and insulin.
- Ultrasound: Looking for the presence of multiple ovarian cysts.
Treatment Options and Lifestyle Changes
While there’s no cure for PCOS, there are several ways to manage its symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some treatment options and lifestyle changes that can help:
Medical Treatments:
- Hormonal Birth Control: Helps regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: Reduces symptoms like excess hair growth and acne.
- Metformin: Improves insulin resistance and can help with weight management and menstrual regularity.
- Fertility Treatments: If pregnancy is a goal, medications like clomiphene or letrozole can stimulate ovulation.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid refined sugars and processed foods.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This can help with weight management and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and lower cortisol levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help regulate hormones.
Personal Stories and Coping Strategies
Living with PCOS can be challenging, but many women find ways to manage their symptoms and lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Here are some coping strategies from women who have been there:
- Join Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Keep a Journal: Tracking your symptoms, diet, and exercise can help you identify what works best for your body.
- Educate Yourself: The more you know about PCOS, the better equipped you’ll be to manage it. Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider questions and seek out reliable information.
Resources
For more in-depth information on PCOS and hormonal health, check out these resources:
Final Thoughts
Understanding the role of hormones in PCOS is essential for managing this condition effectively. By recognizing the symptoms and making informed lifestyle choices, you can take control of your health and well-being. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. At AIMA, we’re here to support you with the knowledge, resources, and community you need to thrive. If you have any questions or need more personalized advice, don’t hesitate to reach out.
